What is Asthma? Its Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
By: Waqas Yousaf | Published on: March 2, 2025
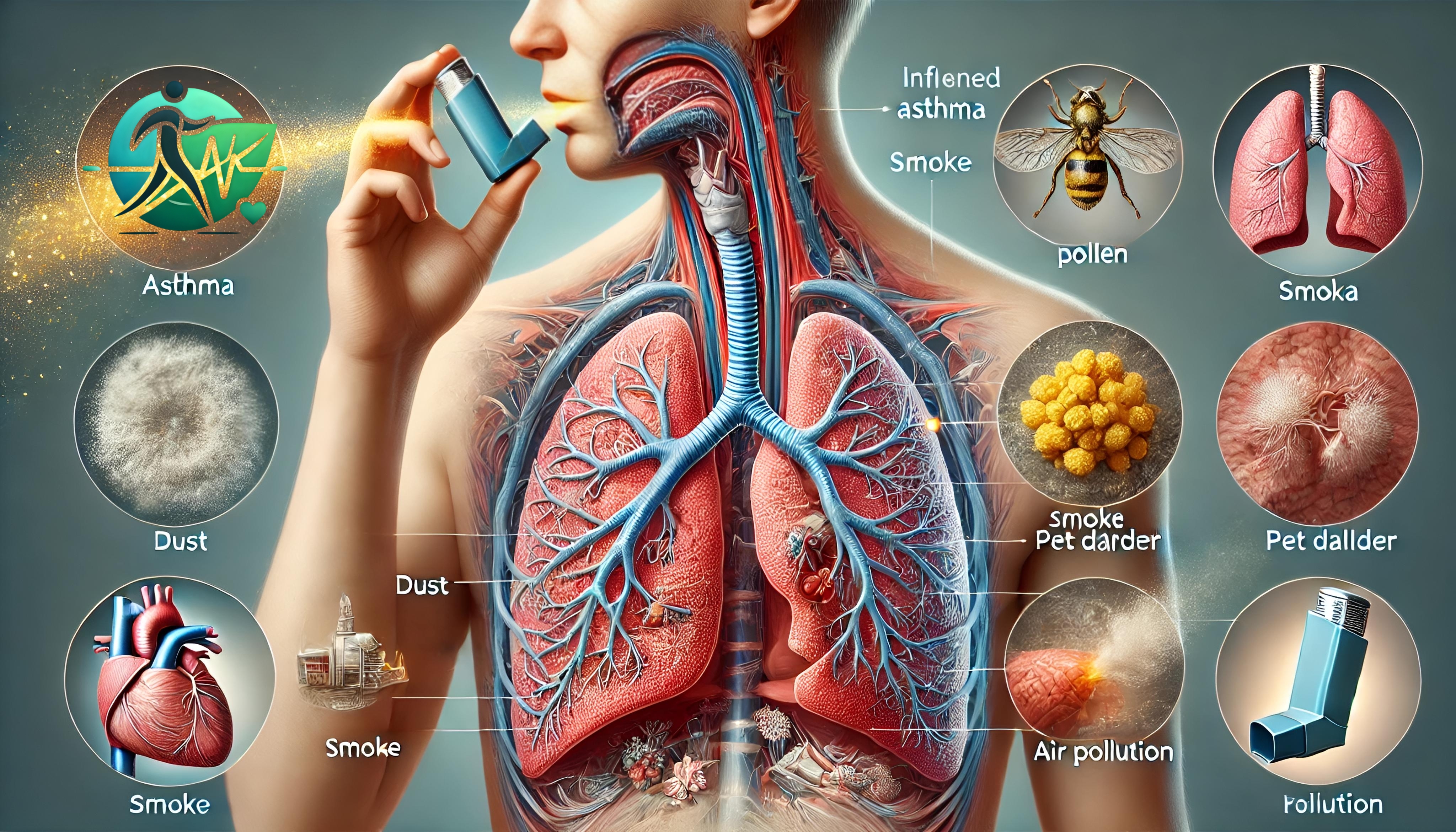
Asthma is a common chronic respiratory disease affecting about 10% of the global population. In Pakistan alone, over 20 million people suffer from asthma.
Why Does Asthma Occur?
Asthma occurs due to an overreaction of the immune system to certain triggers, leading to airway inflammation and narrowing (Type 1 Hypersensitivity). This causes symptoms like wheezing, shortness of breath, coughing, chest tightness, and anxiety.
Common Asthma Triggers
- Environmental factors: Air pollution, dust, pollen, smoke, strong perfumes.
- Medical factors: Respiratory infections, certain medications (aspirin, beta-blockers).
- Weather conditions: Cold air, dry weather.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, stress, anxiety, acid reflux.
Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms vary in severity and can come and go. An asthma "attack" occurs when symptoms suddenly worsen due to airway inflammation.
- Wheezing (whistling sound while breathing).
- Coughing, especially at night or after exercise.
- Shortness of breath and chest tightness.
- Difficulty sleeping due to breathing issues.
- White phlegm-producing cough.
- Allergy symptoms like sneezing and itchy skin.
- In severe cases, blue lips or nails due to oxygen deficiency.
Causes of Asthma
Asthma can be hereditary, and triggers vary among patients. The primary causes include:
- Allergic Asthma: 90% of cases are allergy-related (dust, pollen, pet dander, mold, chemicals).
- Medication-Induced Asthma: Certain drugs like aspirin and beta-blockers.
- Environmental & Weather Factors: Cold air, seasonal changes.
- Lifestyle & Health Factors: Smoking, intense exercise, stress, acid reflux.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Asthma is diagnosed through medical history, symptoms, and tests such as:
- Serum IgE Antibody Test: Identifies allergic reactions.
- Pulmonary Function Test (Spirometry): Measures lung capacity and asthma severity.
- Chest X-ray & Blood Tests: Used if infection or pneumonia is suspected.
Asthma Medications
Treatment varies based on symptom severity. The two main types of medications are:
- Quick-Relief Medications: Rescue inhalers for immediate symptom relief.
- Long-Term Control Medications: Prevent asthma attacks over time.
Common treatments include inhalers, oral medications, and nebulizers. Always consult a doctor before starting medication.
Asthma Prevention and Management
To effectively manage asthma, patients should avoid known triggers. Key prevention tips include:
- Avoid smoke, air pollution, dust, and pollen.
- Stay away from strong chemicals, perfumes, and extreme weather conditions.
- Limit exposure to pet dander if allergic.
- Manage stress, anxiety, and acid reflux to prevent flare-ups.
Asthma is manageable with the right precautions and treatment. By understanding triggers, taking prescribed medications, and making lifestyle adjustments, asthma patients can lead healthy, active lives.
Tags: Superfoods Heart Health Chest Pain Smoke
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Leave a Comment
Recent Articles
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
- Anti-Aging Superfoods: A Profitable Trade for Youthful Skin and Strong Hair
- Requirements for Healthy Sperm and Ways to Improve Male Fertility
- Fruits That Help Overcome Anemia
- Urinary Tract Pain in Women – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!